Photoconductivity – Definition, Working and its Applications
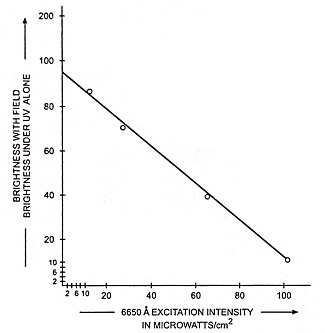
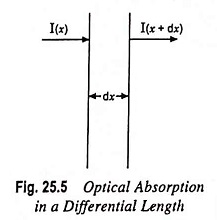
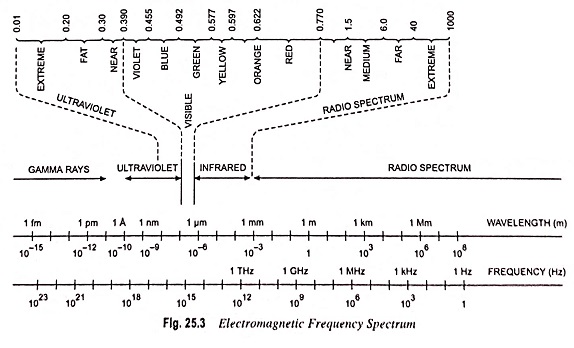
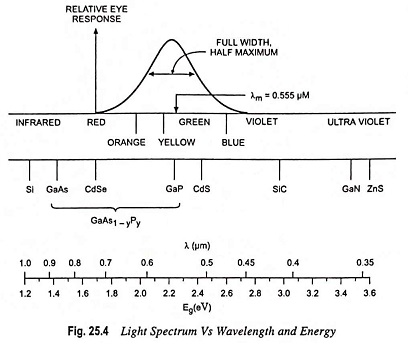
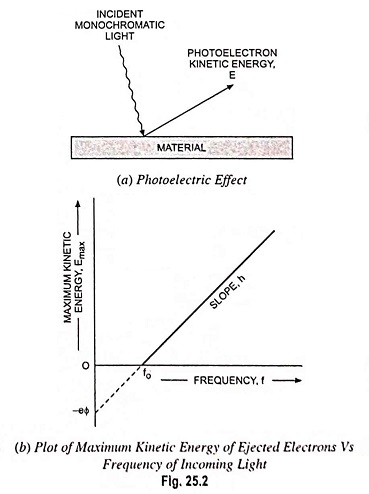
Photoconductivity - Definition, Working and its Applications: Photoconductivity - When excess electrons and holes are produced in a semiconductor, there is a corresponding increase in conductivity of a sample as indicated by the following equation…