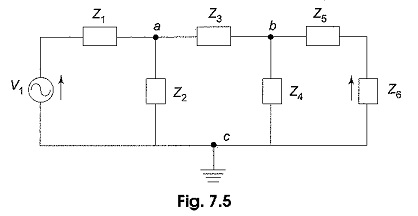
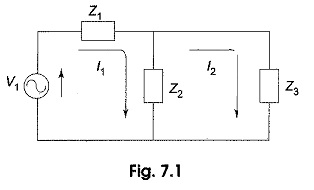
Maximum Power Transfer Theorem
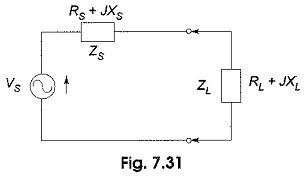
Maximum Power Transfer Theorem: Here, the maximum power transfer theorem has been discussed for resistive loads. The maximum power transfer theorem states that the maximum power is delivered from a source to its load when…