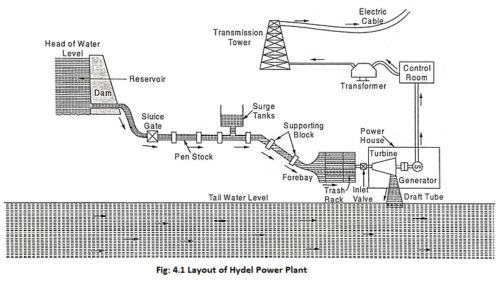
Hydel Power Plant – Definition, Working Principle and Advantages
Hydel Power Plant - Definition, Working Principle and Advantages: Power of water - Hydel Power Plant is a clean and cheap source of energy. The basic principle of hydropower is that when water is piped from…