Protection Principles and Components Articles:
Methods of Discrimination in Power System Protection: Methods of Discrimination in Power System Protection are basically of two types: those which discriminate as to the location of fault, and those which discriminate as to the type of fault. Methods Discriminative to Fault Location: The … (Read More)
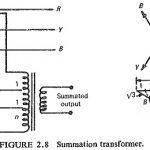
Derivation of Single Phase Quantity from Three Phase System: It will be seen later that auxiliary channels or pilot wires are used to transmit information from one end of the line to the other end. For a normal three-phase system three … (Read More)
Components of Protection System: Some of the more commonly used Components of Protection System are Relays Circuit Breakers Tripping and Other Auxiliary Supplies Current Transformer (CT) Voltage Transformers (VT) Linear Coupler Relays: The main function of a protective relay is to isolate a faulty section with the least interruption … (Read More)