Electromechanical Energy Articles:
Energy in Magnetic System: The chief advantage of electric energy over other forms of energy is the relative ease and high efficiency with which it can be transmitted over long distances. Its main use is in … (Read More)
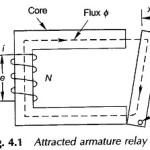
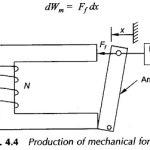
Field Energy and Mechanical Force: Consider once again the attracted armature relay excited by an electric source as in Fig. 4.4. The field produces a mechanical force Ff in the direction indicated which drives the … (Read More)
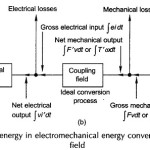
Principle of Electromechanical Energy Conversion: Principle of Electromechanical Energy Conversion is a reversible process and Eqs (4.26) to (4.29) govern the production of mechanical force. In Fig. 4.4 if the armature is allowed to move on positive x direction under the influence … (Read More)
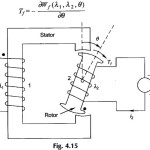
Multiply Excited Magnetic Field System: Singly-excited devices discussed earlier, are generally employed for motion through a limited distance or rotation through a prescribed angle. Electro-mechanical transducers have the special requirement of producing an electrical signal proportional … (Read More)
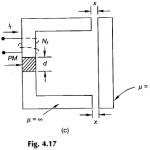
Forces in system with Permanent Magnets: Method of finding Forces in system with Permanent Magnets is best illustrated by an example. Figure 4.17(b) shows a moving armature relay excited by a permanent magnet (PM). The dc magnetizing curve of the permanent magnet … (Read More)
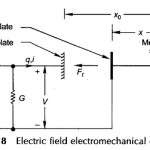
Electromechanical Energy Conversion via Electric Field Energy: Electromechanical energy conversion via the electric field is analogous to the magnetic field case studied earlier. Charge in the Electric Field Energy is analogous to flux linkages and voltage to current in the magnetic … (Read More)
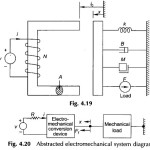
Dynamical Equations of Electromechanical Systems: Figure 4.19 shows an electromagnetic relay whose armature is loaded with spring K, damper B, mass M and a force generator F. Figure 4.20 shows the abstracted diagram of a general … (Read More)