Motor Power Rating Articles:
Selection of Motor Power Rating: The Selection of Motor Power Rating of a motor for a specific application must be carefully chosen to achieve economy with reliability. Use of a motor having insufficient rating, either fails to drive the load at … (Read More)
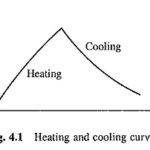
Heating and Cooling Curves of Electrical Drives: An accurate prediction of Heating and Cooling Curves of Electrical Drives rise inside an electrical motor is very difficult owing to complex geometrical shapes and use of heterogeneous materials. Since conductivities of various materials … (Read More)
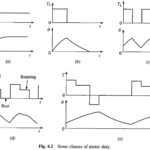
Classes of Motor Duty in Electrical Drives: IS: 4722-1968 categorises various load time variations encountered in practice into eight standard Classes of Motor Duty in Electrical Drives: Continuous duty. Short time duty. Intermittent periodic duty. Intermittent periodic duty with starting. Intermittent periodic duty with starting and … (Read More)
Motor Rating Various Duty Cycles: From the point of view of calculation of motor rating various Motor Rating Various Duty Cycles can be broadly classified as: Continuous duty. Fluctuating loads. Short-time and intermittent duty. Continuous Duty: Maximum continuous power demand of the load is ascertained. A … (Read More)