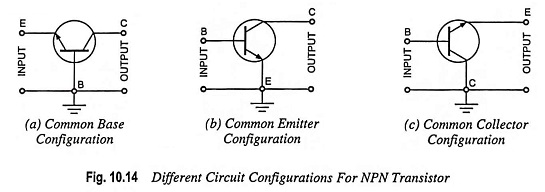
Transistor Circuit Configurations (CB, CE, CC)
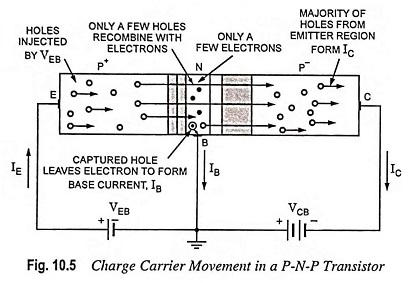
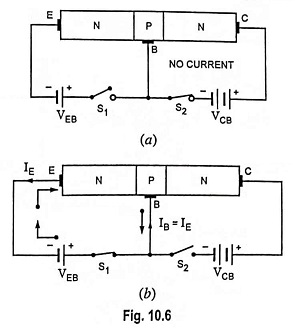
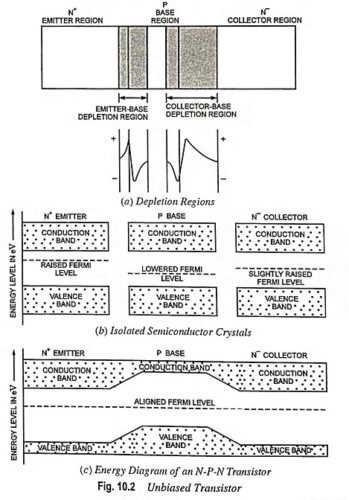
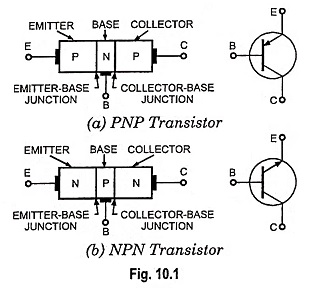
Transistor Circuit Configurations (CB, CE, CC): As already mentioned, a Transistor Circuit Configurations is a three-terminal device (having three terminals namely emitter, base and collector) but we require four terminals—two for the input and two for the output for connecting it in a circuit. Hence one of the terminals of the transistor is made common […]
Transistor Circuit Configurations (CB, CE, CC) Read More »