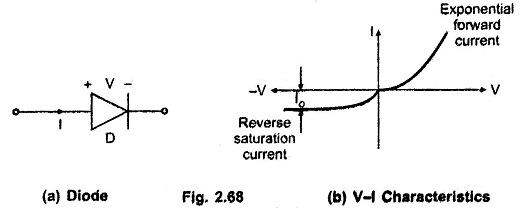
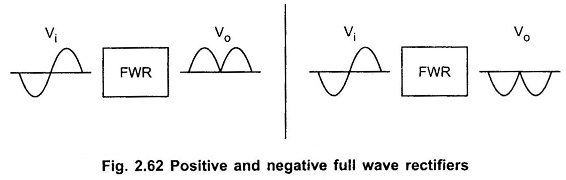
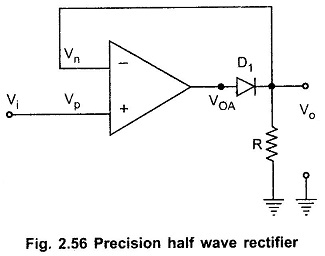
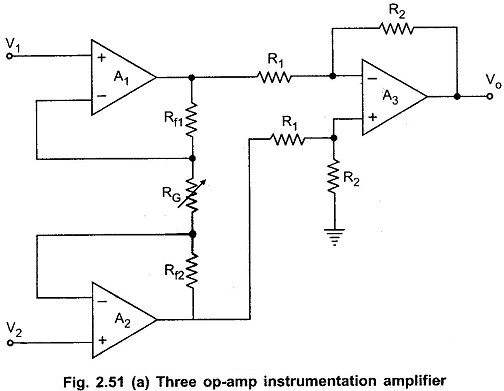
Filters in Linear Integrated Circuits
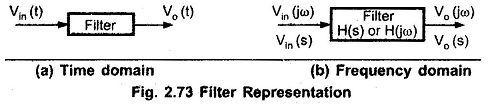
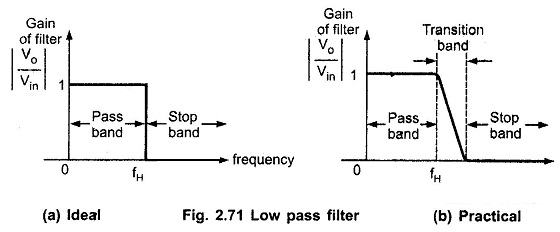
Filters in Linear Integrated Circuits: The Filters in Linear Integrated Circuits can be represented in the time domain and frequency domain as shown in Fig. 2.73 (a) and (b). As the filter is frequency selective…