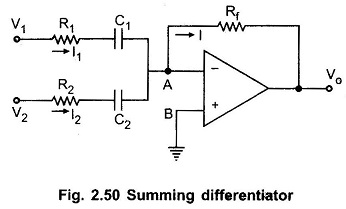
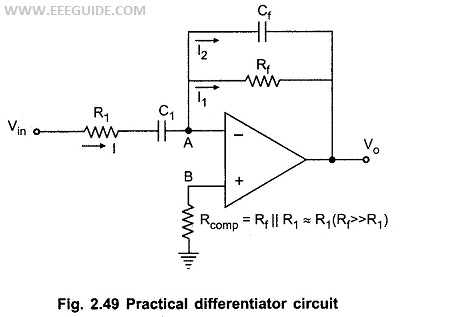
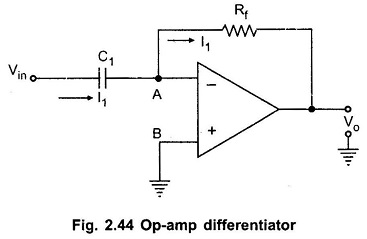
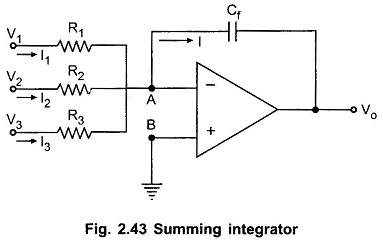
Instrumentation Amplifier or Data Amplifier
Instrumentation Amplifier or Data Amplifier: Instrumentation Amplifier – Many industrial systems, consumer systems and process control systems require a precise measurement of the physical quantities like temperature, pressure, humidity, weight etc. A sugar factory requires a measurement of flow, level and temperature of juice. The plastic furnaces require precise measurement of the temperature. The dairy […]
Instrumentation Amplifier or Data Amplifier Read More »