Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM)
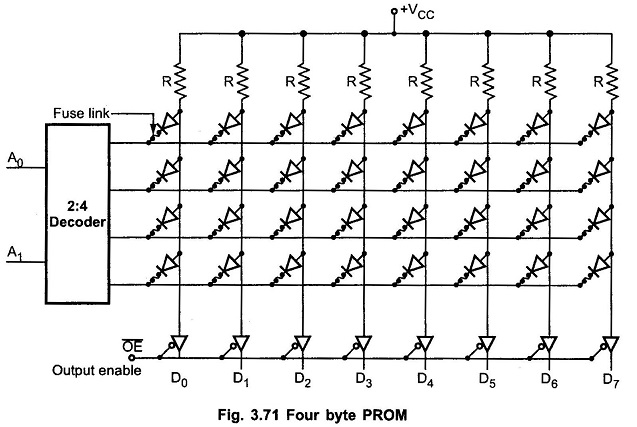
Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM): Fig. 3.71 shows four byte Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM). It has diodes in every bit position; therefore, the output is initially all 0s. Each diode, however has a fusible link in series with it. By addressing bit and applying proper current pulse at the corresponding output, we can blow […]
Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM) Read More »