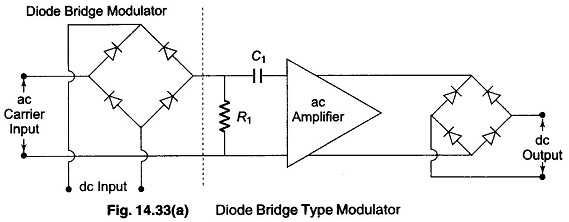
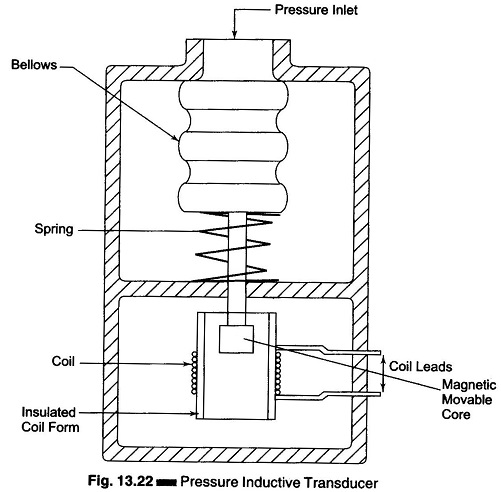
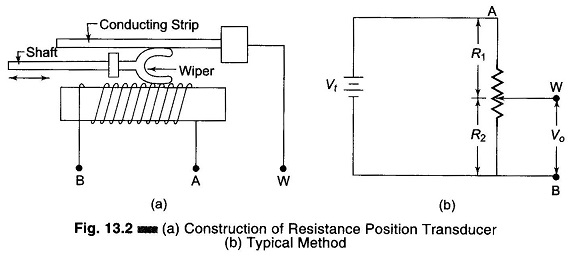
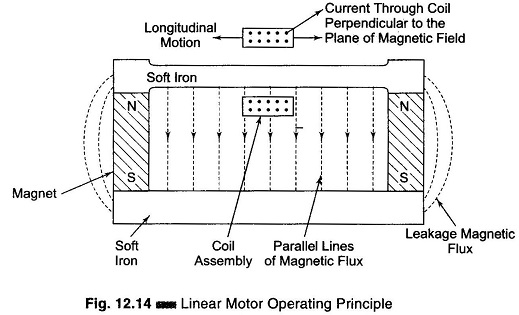
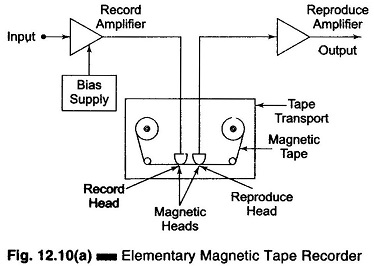
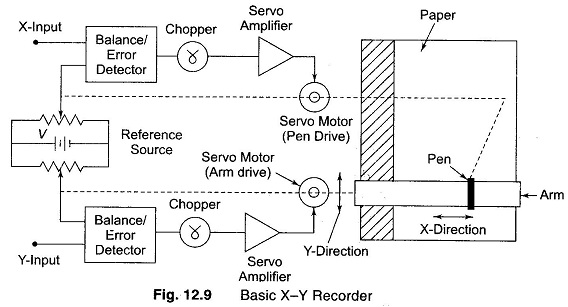
Data Acquisition System
Data Acquisition System: A typical Data Acquisition System consists of individual sensors with the necessary signal conditioning, data conversion, data processing, multiplexing, data handling and associated transmission, storage and display systems. In order to optimise the characteristics of the system in terms of performance, handling capacity and cost, the relevant sub systems can be combined […]
Data Acquisition System Read More »