Circular Chart Recorder Working Principle
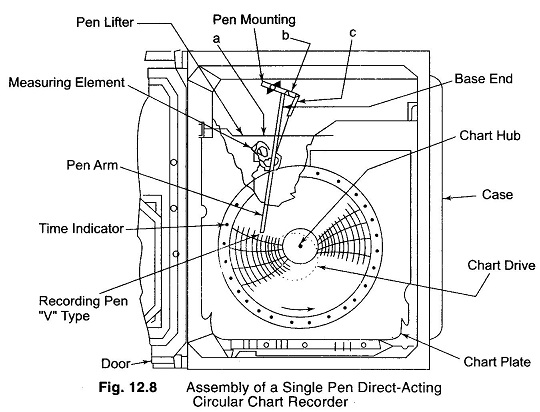
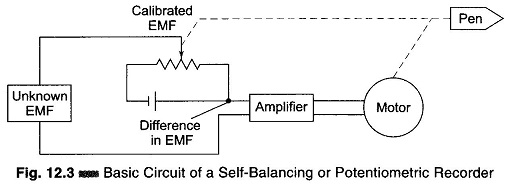
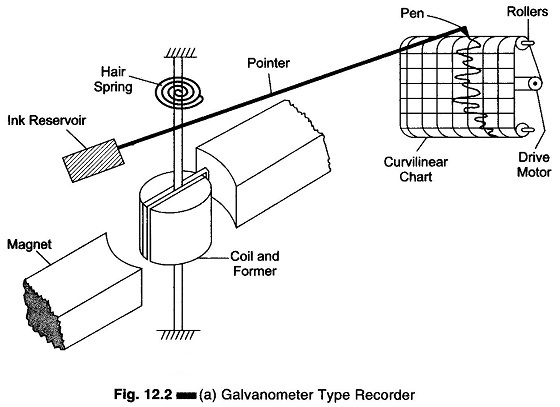
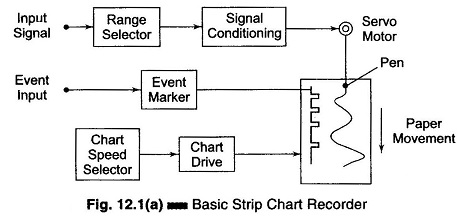
Circular Chart Recorder Working Principle: Circular Chart Recorder Working Principle – As the name implies, the data is recorded on a flat circular chart. The basic assembly of a single pen circular chart recorder is shown in Fig. 12.8. It consists of a measuring element, an operating mechanism, a chart drive, and a recording device, […]
Circular Chart Recorder Working Principle Read More »