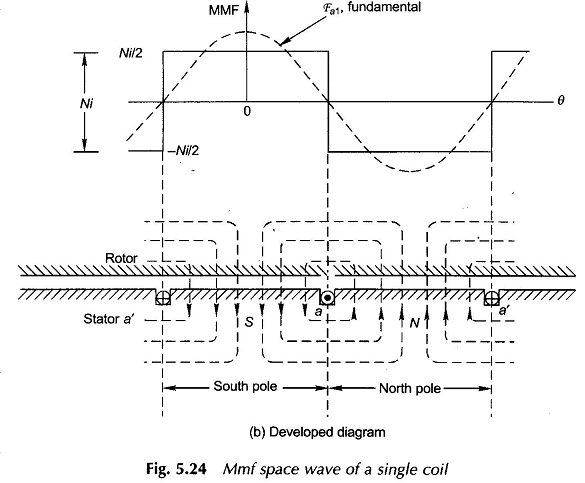
MMF of AC Distributed Winding
MMF of AC Distributed Winding: It has been seen earlier that the armature what-when-how.comof a practical machine has distributed winding wound for the same number of poles as the field winding. As the armature carries current, the resultant field of its current-carrying coils has the same number of poles as the field winding. Our approach […]
MMF of AC Distributed Winding Read More »