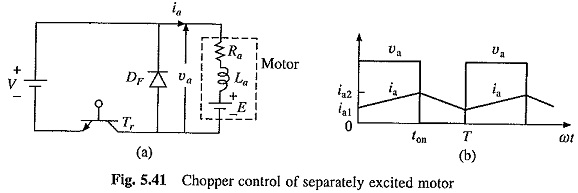
Chopper Control of Series Motor:
Motoring : Chopper Control of Series Motor and va and ia waveforms will be same as shown in Fig. 5.41. Va is given by Eq. (5.113).
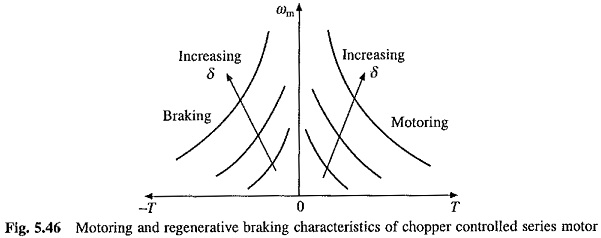
However, e is not constant but varies with ia. Due to saturation of magnetic circuit, relationship between e and ia is non-linear. The approximation is already described and is applicable here. Consequently, motor performance can be calculated. The nature of speed torque curves is shown in Fig. 5.46.
Regenerative Braking:
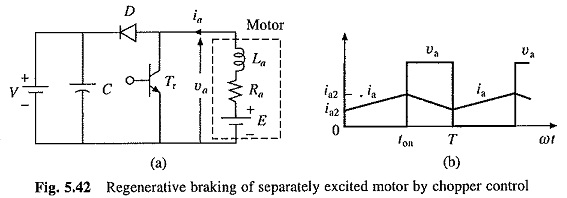
With Chopper Control of Series Motor, regenerative braking of series motor can also be obtained. Power circuit of Fig. 5.42(a) is employed. During regenerative braking, series motor functions as a self-excited series generator. For self-excitation, current flowing through field winding should assist residual magnetism. Therefore, when changing from motoring to braking connection, while direction of armature current should reverse, field current should flow in the same direction. This is achieved by reversing the field with respect to armature when changing from motoring to braking operation. Waveforms of va and ia will be same as those of Fig. 5.42(b).
Approximation of Equation is applicable here. From Fig. 5.42(a)
For a chosen value of Ia, Ka is obtained from magnetization characteristic. Then T and ωm are obtained from Eqs. (5.125) and (5.124), respectively. The nature of speed-torque characteristics is shown in Fig. 5.46. Such characteristics give unstable operation with most loads. Consequently, regenerative braking of the series motor is difficult.
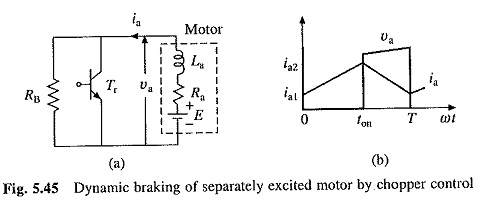
Dynamic Braking:
Chopper Control of Series Motor for Dynamic Braking is shown in Fig. 5.45(a) is used. Since motor works as a self-excited generator, when changing from motoring to braking, field should be reversed.