Precision Rectifiers
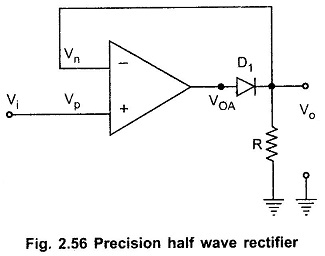
Precision Rectifiers: Recall from basic circuit principles that a rectifier circuits can be implemented with a diode/diodes (half wave rectifier or full wave rectifier). The major limitations of these Precision Rectifiers circuits is that they cannot rectify voltages below VD(ON) = 0.7 V, the cut-in voltage of the diode. In these circuits Vi has to […]
Precision Rectifiers Read More »