Nuclear Fission and Nuclear chain reaction
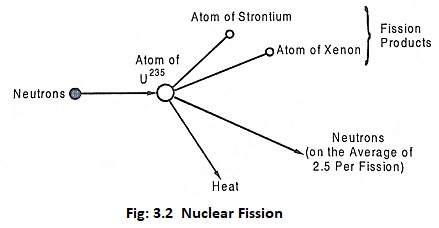
Nuclear Fission and Nuclear chain reaction: Uranium exists in different isotopes of U238, U234 , and U235. Out of these, U235 is the most unstable. When unstable heavy nucleus is bombarded with high energy neutrons, it splits up roughly into two equal fragments and about 2.5 neutrons are released and a large amount of energy is produced […]
Nuclear Fission and Nuclear chain reaction Read More »